..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Dynamic variables and List
Number
int var_name;
double var_name;
why dclare type case language in dart
hold the data types dynamic and Static
Do (Rights) | Don't( Wrongs)
-------------------------------------------
int alpha99 | int 99alpha
int _name | int @name
int $name | int &name
| int #name
...................................................
var name =4;
print(name);
...................................................
var name =4;
name ='Johan'
print(name);
//Error: A value of type 'String' can't be assigned to a variable of type 'int'.
...................................................
When are you not sure with type of data is coming , So that cases declare as variable like that
var name;
name =44;
name ='Johan Doe';
print(name);
..................................................
Example: #1
dynamic firstName='Johan';
firstName=40;
print(firstName);
Example: #2 [dynamic]
List name=['Johan', 'Smith'];
print(name);
Example: #3
List job=[];
job.add('Software');
job.add(22);
print('$job');
Example: #4
List fruits=['Banana', 'Orange'];
fruits.add('KIWI');
fruits.add(22);
print(fruits);
or
print('$fruits');
..........................................................................
List<dynamic>name =['Johan', 'Smith', 33];
name.add(22);
print(name);
Example: #5 [ for loop ]
List<String> name=[];
for(int i=0;i<1; i++){
name.add('Hello World, ${i}');
print('$name');
or
print(name);
Example: #6[ add a different type ]
List <int> name=['Johan', 'Smith'];
print(name);
// Error: A value of type 'String' can't be assigned to a variable of type 'int'
..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Map [ dynamic ]
Example :#1
Map maps ={
"key": 'One Value',
2: 'Two Value'
};
print(maps);
Example :#2 [ Key, Value ]
Map<Key, value>
ie Key is key, 2,
Value is One Value, Two Value
Map <dynamic, String> maps ={
"key": 'One Value',
2: 'Two Value'
};
print(maps);
Example :#3 [ remove Duplicate, Values, Keys, toList, ]
Map <dynamic, String> maps ={
1:'Prince',
2:'Smith',
3: 'Johan'
};
print(maps.values);
..........................................................
Map <dynamic, String> maps ={
1: 'Prince',
2: 'Smith',
3: 'Johan'
};
print(maps.keys);
Map <dynamic, String> maps ={
1:'Prince',
2:'Smith',
3: 'Johan'
};
print(maps.keys.toList()); //[1, 2, 3]
..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
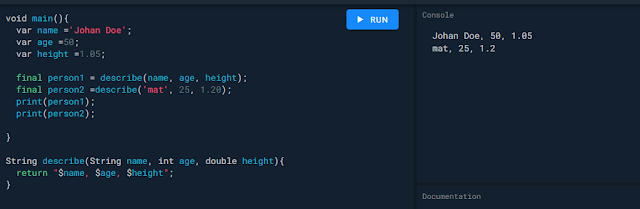
Expression or interpolate
Example :#1
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "world";
String res = str1+str2;
print("The concatenated string : ${res}");
Example :#2
String str1 = 'this is a single line string';
String str2 = "this is a single line string";
String str3 = '''this is a multiline line string''';
String str4 = """this is a multiline line string""";
print(str1);
print(str2);
print(str3);
print(str4);
Example :#3
print('${2+2}');
Example :#4
int n=1+1;
String str1 = "The sum of 1 and 1 is ${n}";
print(str1);
String str2 = "The sum of 2 and 2 is ${2+2}";
print(str2);
Example :#3 [final vs const ]
Dart throws an exception if an attempt is made to modify variables declared with the final or const keyword. The example given below illustrates the same -
Compile-time constants are constants whose values will be determined at compile time
if you never want to change a value then use fianl and const keywords
Difference between final and const ?
final variable can only be set once and it is initialized when accessed.
final name ="Peter" ;
final cityName ='Mumbai';
cityName ='Dubai';
//Error
const vriable is implicitly final but is a compile-time constants
> ie it is initialized during compilation
const pi =3.14
when you compile your program, in that sistutations pi will be initialized memory will be allocated.
ie consumed memory; no matter you are using pi in the program or not
instance variable can be final but cannot be const. or ie static const
like Example
class Circle{
final color='red';
//const PI=3.14;
static const PI=3.14;
}
its optional
final String cityName ='Mumbai';
const PI =3.14;
optional
const double PI =3.14;
..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
What is singleton pattern ?
- One of the simplest design pattern
- There can only be one instance of the class
- class itself is responsible to keep track of its sole instance
- The instance is globally accessible through static method
- Constructor is private so it cannot be instantiated
Dart is single threaded language
- should bethread safe
- signleton class shouldn't require any params
void main(){
for (int i=0; i<5;i++){
print('Hello ${i+1}');
}
final getname = Singleton.instances;
print(getname.name);
}
class Singleton{
String name;
static Singleton _instance;
Singleton._internal(){
name ='Single patterndd';
}
static Singleton get instances {
if(_instance == null){
_instance = Singleton._internal();
}
return _instance;
}
}
..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
int getAge()=> 30;
same as
int getAge(){
return 30;
}
Type checked
List
Functions
void = not returns
String
NULL
Arrow operators =>
void sayName(String name)=>print('Hello I'm '$name');
cascade
List list = [];
list.add(color1);
list.add(color2);
list.add(color3);
list.add(color4);
// with cascade
List list = [];
list
..add(color1)
..add(color2)
..add(color3)
..add(color4);
.............................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Class with Assert
void main() {
final user = User(age:25, name:"Johan");
print(user.age);
}
class User {
int age;
String name;
User({this.age, this.name});
}
void main(){
final user =User();
print(user.getAge);
}
class User {
int get getAge => 500;
}


















No comments:
Post a Comment